A “pest detection system” described in a recently published patent application is claimed to provide localized extermination of bed bugs through mimicry of a human presence.
Bed bugs are small, parasitic creatures that are notorious for biting people while they are asleep, and seemingly vanishing during the day. They are difficult to detect and capable of spreading across households, apartments, or offices. These insects are nocturnal and able to detect when a potential host is emitting carbon dioxide. Their elusive nature can lead to infestations that go unnoticed for a very long time.
One reliable method of ending these infestations is chemical fumigation. Unfortunately, this approach is expensive and requires sealing entire rooms, if not entire dwellings. This is because the chemical deployed, sulfuryl fluoride, is highly toxic. This colorless, odorless gas is also used to control other pests like termites and rats.
Inventors from Atlanta-based Cortland IP suggest an alternative to the conventional, large-scale approach to bed bug infestations. They designed a system with components to imitate human temperature, respiration, and odor, along with one or more trapping mechanisms for the insects.
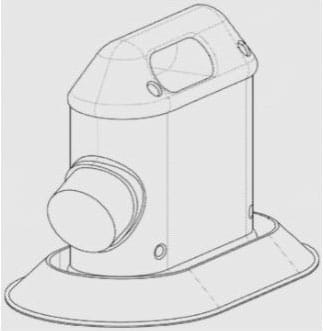
Illustration of an exemplary pest detection system
The temperature component may come in the form of any suitable heating element configured to radiate a desired temperature, possibly similar to that of the average human body, which is about 98°F.
To mimic human respiration, a gas emitter system may be configured to emit carbon dioxide, or other suitable gases, from an attached tank. The component may be configured to emit the gas continuously, periodically in particular amounts, or even in a selected human breathing pattern.
Another way the device might draw out bed bugs is by releasing one or more human pheromones from its odor component. The patent application mentions a pheromone tray, which may be installed in a way that precludes access to trapped pests.
The system may be constructed with any suitable number of trapping components. Cortland IP lists a foothold trap, a body-gripping trap, a snare, a deadfall trap, a cage, a trapping pit, and a glue trap as possible options.
Operating and monitoring the above components is done through a control system, which may come with suitable input mechanisms such as buttons, switches, or a touch screen. The screen may be configured to display desired information about the pest detection system.
The featured patent application, “Method and System for Infestation Detection”, was filed with the USPTO on January 8, 2021 and published thereafter on July 15, 2021. The listed applicant is Cortland IP, LLC. The listed inventors are Rene Gomez and Liam Carson Tremblay.






