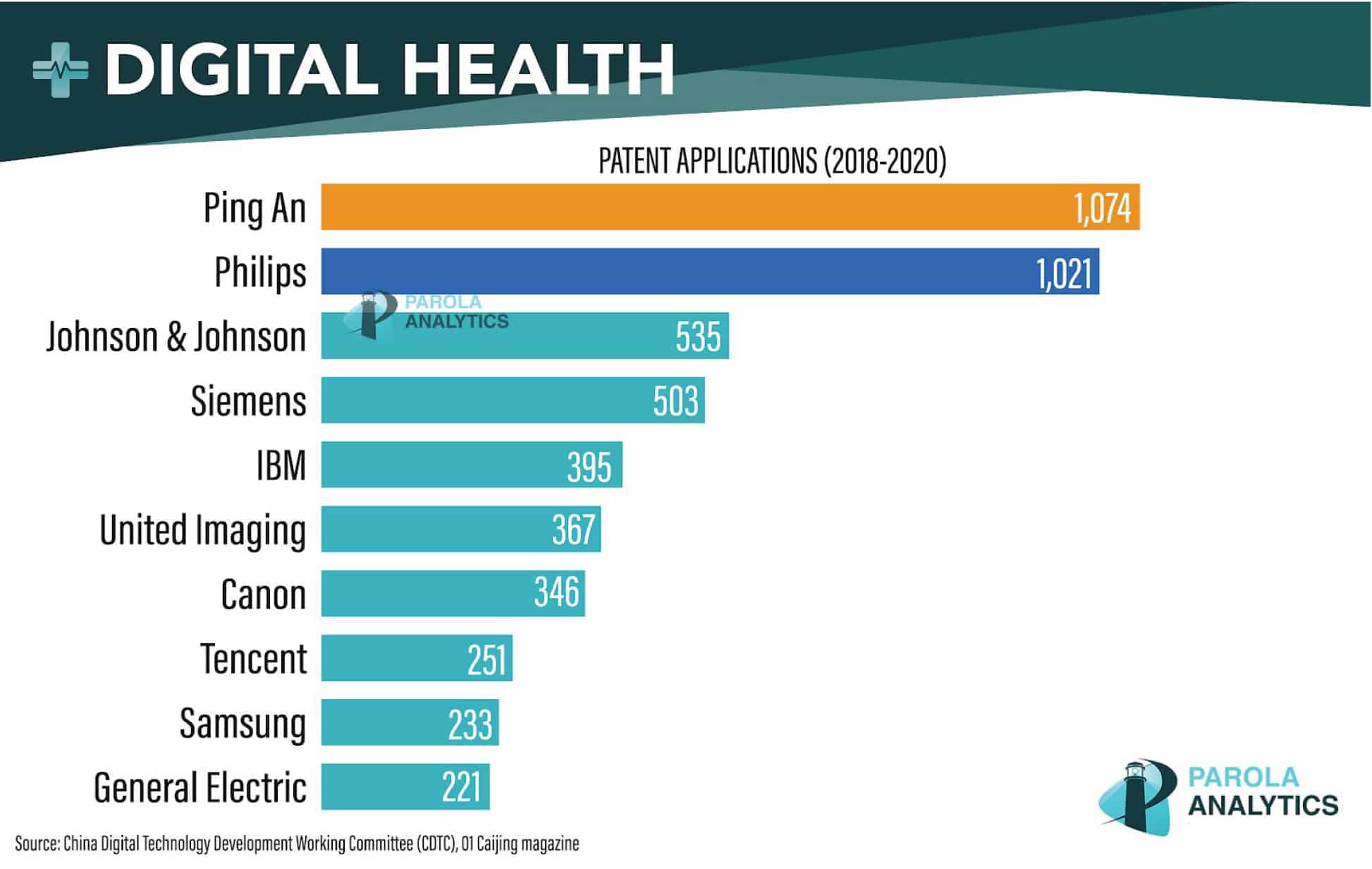
Ping An Insurance Group and Philips were the world’s most prolific digital health patent applicants in the last three years, according to the China Digital Technology Development Working Committee (CDTC).
The report, jointly issued with 01 Caijing magazine, says the Chinese financial services company filed 1,074 patent applications between 2018 and 2020. Netherlands-based Philips trailed it with 1,021 filings. Healthcare giant Johnson & Johnson came in third by a wide margin, at 535 digital health patent applications. Ping An says its digital health patent applications from the last three years mainly contained claims for smart diagnosis, treatment assistants, patient record management, medical image processing, medicine management, and smart hospital management.
Meanwhile, Philips boasts a €1.9 billion R&D program that has recently patented innovative CT imaging and MRI systems, as well as patient monitors and even smart power toothbrushes. The company is also in the process of acquiring BioTelemetry Inc., a U.S.-based provider of remote cardiac diagnostics and monitoring. The €2.3-billion deal is expected to bolster Philips’ portfolio with wearable heart monitors as well as AI-based data analytics and services.
The CDTC report also noted the growing digital health footprint of companies outside the healthcare industry. Tencent was the other Chinese company among the top ten digital health patent filers. Like Ping An, Tencent mainly operates outside the health sector, specifically in internet and entertainment.
Digital health spans the widening range of technology that employs computing, connectivity, software, and sensors to deliver medical data and improve outcomes. From health monitoring software in wearable devices to AI-powered platforms that inform doctors’ clinical decisions, the digital health industry and its products have become increasingly ubiquitous; all of it is set to be worth US$833.44 billion by 2027.