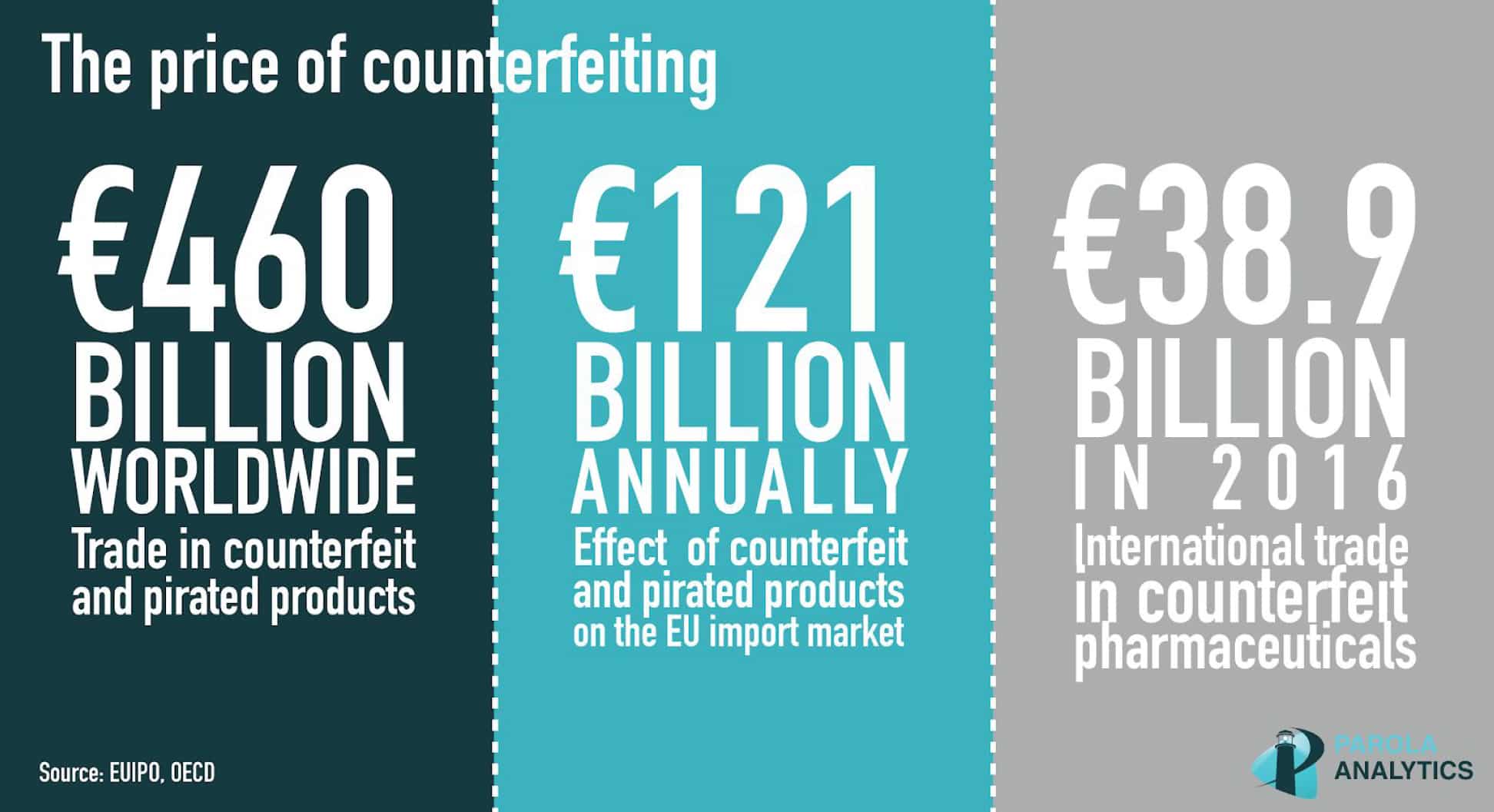
In a 2022 report by IBM, the global total average cost of a data breach was estimated to be around $ 4.35 million with the US having the greatest loss among the rest. It was also found that it took an average of 277 days for a breach to be identified and contained. These numbers alone are enough motivation to strengthen cybersecurity measures within an organization.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) considers zero-trust as “a cybersecurity paradigm focused on resource protection and the premise that trust is never granted implicitly but must be continually evaluated.” Never trust, always verify. This is the zero-trust motto that aptly describes this cybersecurity model that will be the unifying theme of the patent applications discussed in this article.
Zscaler | Cloud-based deception technology utilizing zero trust to identify threat intelligence, telemetry, and emerging adversary tactics and techniques
Deception technology is a cybersecurity solution that relies on fake assets strategically positioned throughout a network to entice cyber assailants. The fake assets serve the purpose of detecting the attacker’s malicious actions without causing any harm to the overall security of the system. Essentially, fake assets have no actual functional value and serve only to alert the system of a possible intrusion once the assets are accessed.
In this patent application, deception technology is implemented into a zero-trust framework by creating fake assets that match the user’s historical patterns. Each user activity is monitored within the network so that fraudulent items are crafted according to their specific needs and interests, similar to how advertisements can be customized based on personalized profiles. Upon trying to access the fake assets, the users will automatically be rerouted towards a cloud-based decoy environment which would isolate the malicious activity in a timely manner. Within the decoy cloud environment, the user activity is further monitored thereby providing the cybersecurity system supplementary information concerning malicious intent tactics during the intrusive attack.
US 2023/0164182 was filed on January 8, 2022 by Zscaler, Inc.
Cisco | Limiting Discovery of a Protected Resource in a Zero Trust Access Model
A faster internet connection and the proliferation of smartphones are probably the most significant technological advancements that led to the widespread adoption of digitalization. By converting business processes into digital format, it became feasible to reduce the time previously taken for manual tasks completion. Moreover, information sharing became more convenient as compared to olden days where paper-printed documents are archived in physical cabinets. These days, those documents are available as digital assets in a cloud storage and are available for viewing anywhere in the world.
Despite the ease and accessibility provided by digitalization, this convenience entails a security risk. As anyone can have access to the internet, it also becomes easy to breach a less secure business enterprise whose data are available in digital form.
This patent application proposes a system for safeguarding electronic information by implementing a zero-trust system that renders digital assets to be undiscoverable by unapproved users. To discover the location of the asset, users must successfully complete an initial authentication procedure through validation of their login credentials. Upon successful login, users may be furnished with tokens enabling them to locate protected digital assets. To obtain access to these files, however, users are required to pass a second authentication process which involves undergoing real-time confirmation procedures such as providing one-time passwords or other secure forms of identification.
US 2023/0126355 was filed on October 21, 2021 by Cisco Technology, Inc.
Sophos | Incremental Enrichment of Threat Data
In April 2022, hackers employing ransomware breached Costa Rica’s Finance Ministry and infected additional governmental systems including the Science, Technology, and Communications Ministry as well as the National Meteorological Institute. Subsequently, this attack interfered with tax collection procedures which caused a disruption in operations whilst also placing their citizens’ personal information at risk resulting in the declaration of a state of emergency by Costa Rican authorities.
It only starts with one machine. If left by itself, ransomware can easily spread to other machines within the network and cripple a system. In Costa Rica’s case, a nation.
The patent application proposes the use of cybersecurity strategies that operate on a network-wide scale that uses zero-trust network access, in conjunction with safeguarding individual machines or computer applications. Analytics regarding malicious activities and corrective actions are consistently collected along with their geographic location. Each malicious activity is properly categorized and assigned a threat score which is calculated based on the data collected for each category. Whenever a particular category exceeds an established score threshold, it initiates an investigation process whereby all pertinent information related to the cyberthreat is presented on a user interface with notifications directed at security personnel overseeing the network’s operations.
US 2023/0114821 was filed on May 26, 2022 by Sophos Ltd.
More on zero-trust security in our 2023 Technology Trends Report.