NASA has long been a pioneer in space technology and exploration, pushing the boundaries of technology to support missions beyond our planet since its foundation in 1958. Since then, the agency has been making and supporting great efforts in many avenues related to space and aeronautics technologies.
One of their latest achievements is the development of advanced autonomous in-space assembly (ISA) technologies, using precise and reliable systems to build structures in space with minimal human intervention.
The Evolution of the Stewart Platform
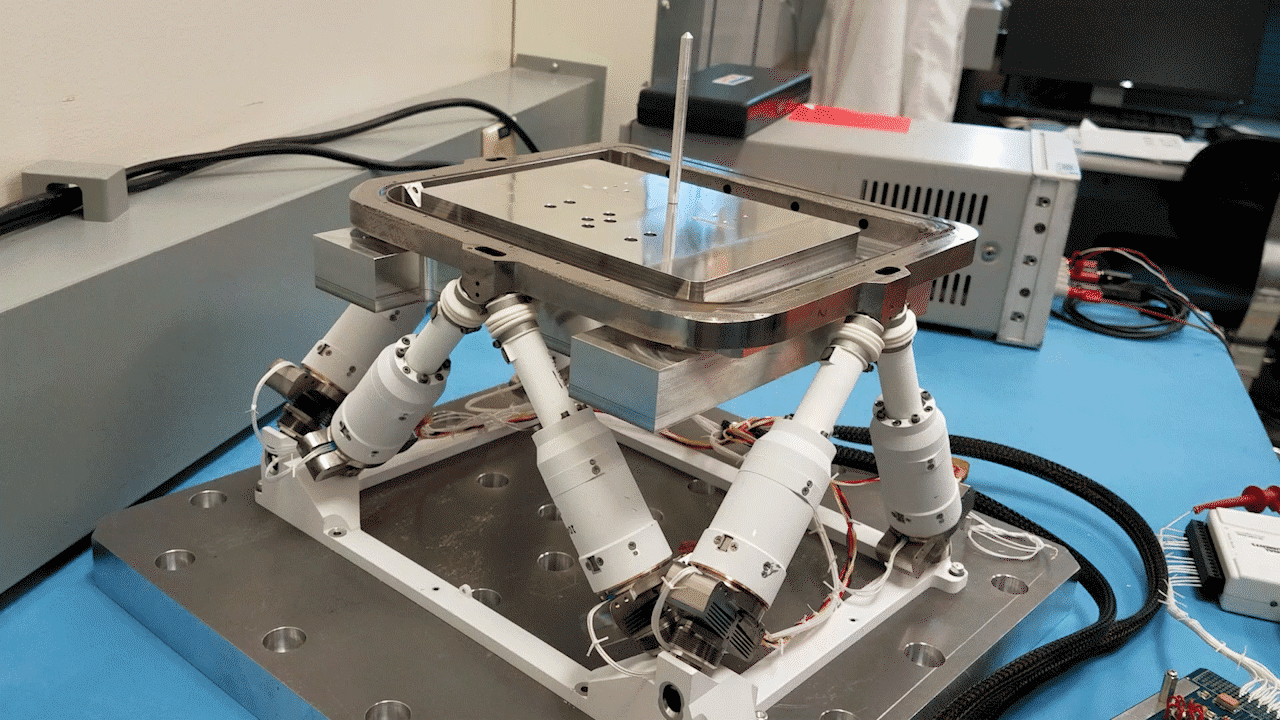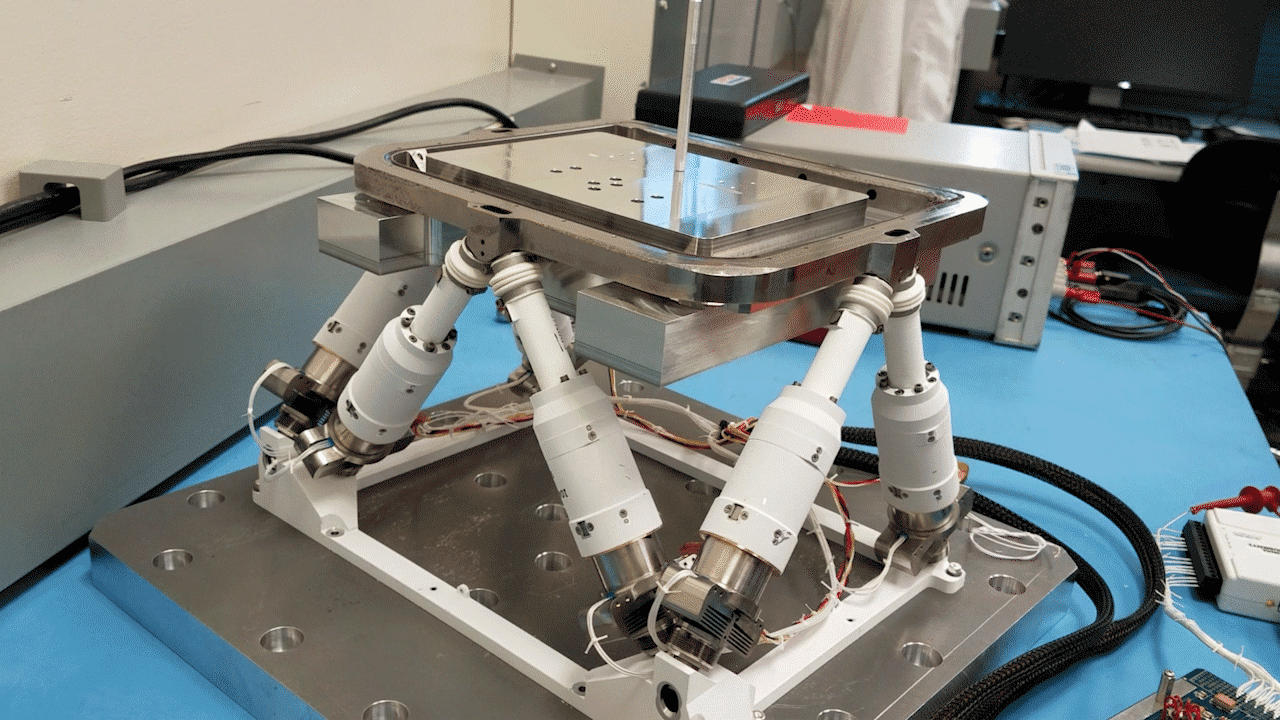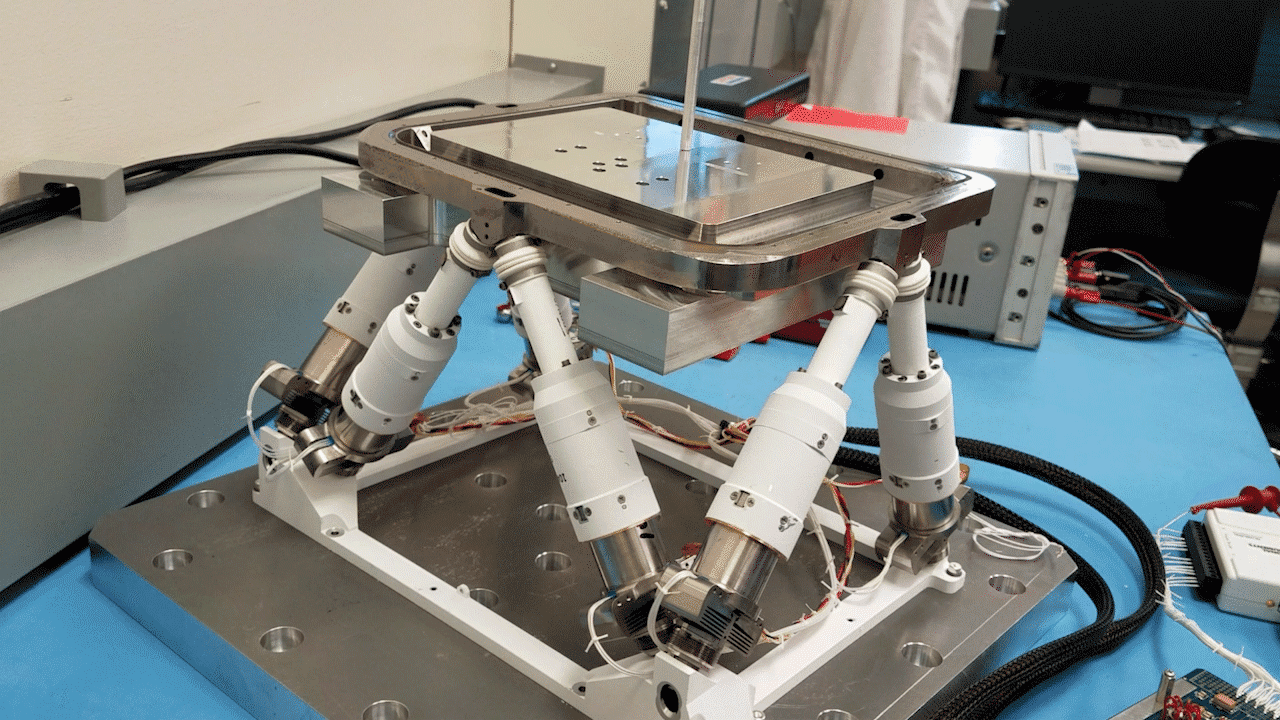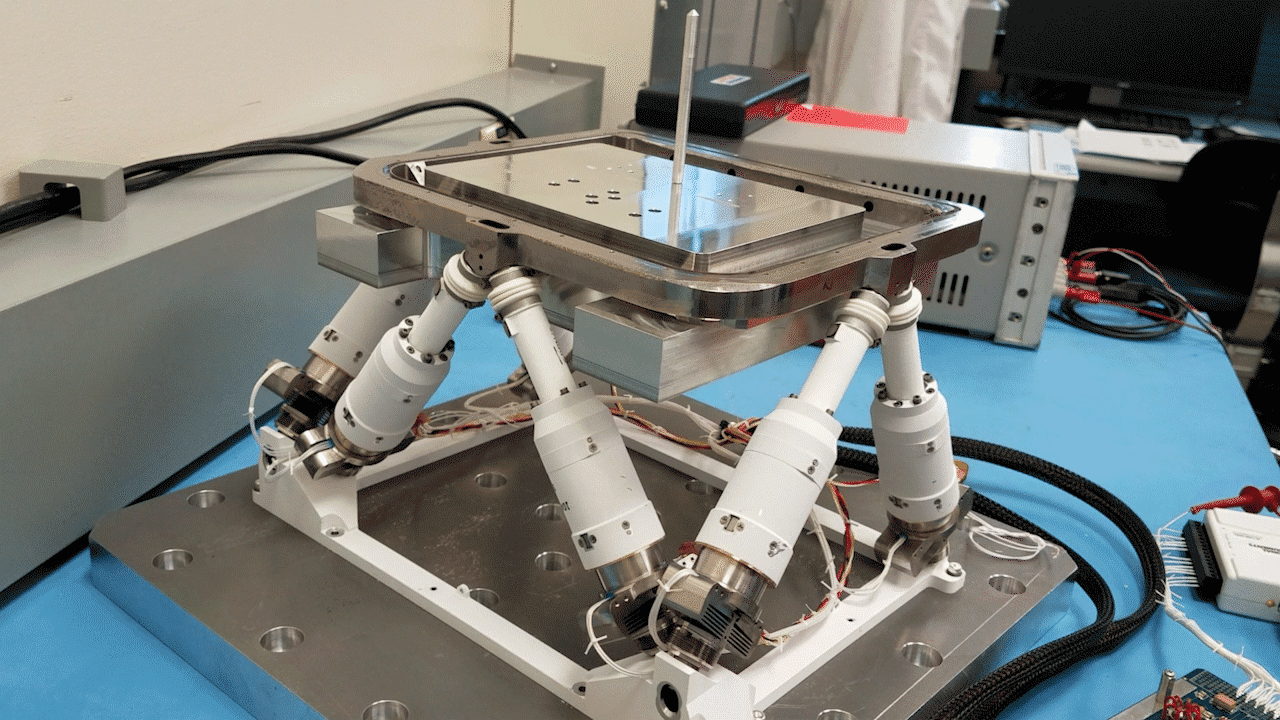
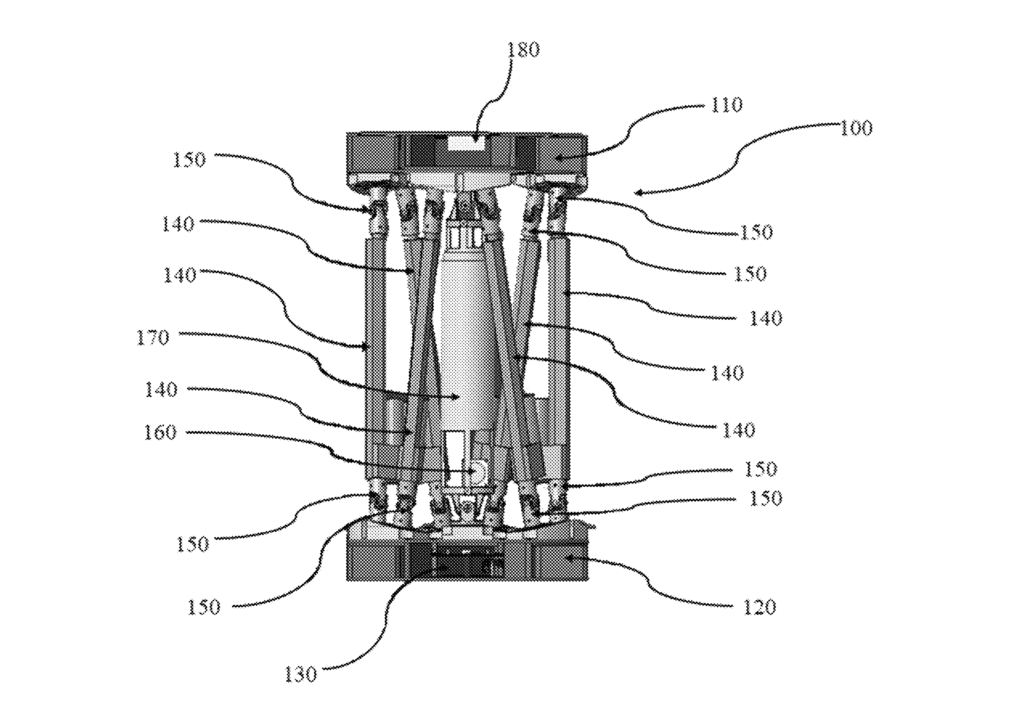
NASA’s recent patented technology is an improvement on the Stewart platform, or hexapod, which was first developed over 50 years ago. The Stewart platform allows for six degrees of freedom, providing high-precision movement. In the 1980s, NASA developed a stacking of these Stewart platforms to extend its capabilities, but the stacked platforms suffered issues in terms of accuracy and precision specifically at the top plate of the stack.
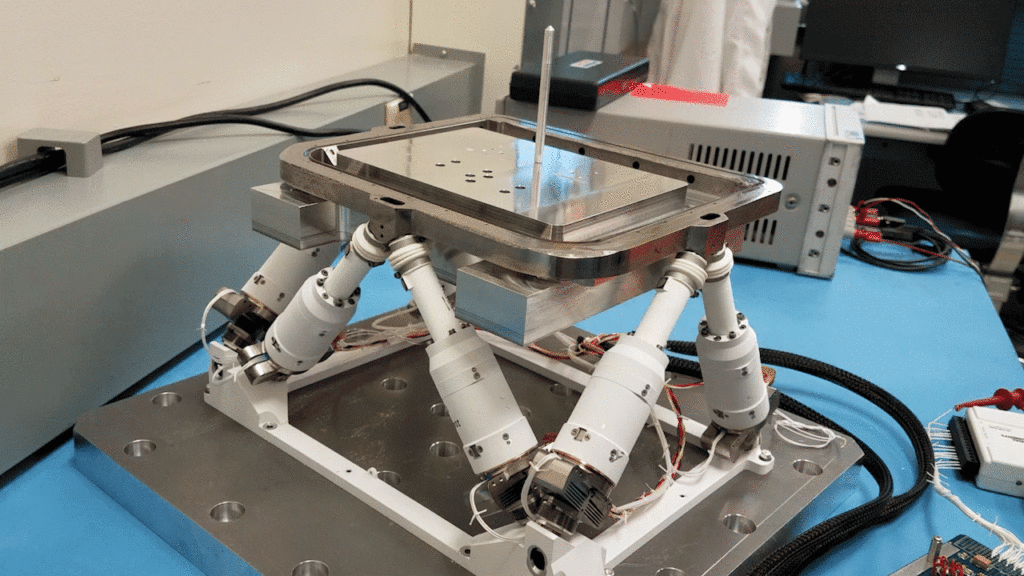
NASA Assembler Patent
However, recent advancements in technologies allow the stacked hexapod platforms to be integrated with modern control theory and machine learning algorithms, allowing NASA to create a more effective and functional iteration of this stacked platform. This innovative technology, patented under U.S. Patent No. 11,989,009 entitled “Modular and reconfigurable assembler system for autonomous in-space assembly” represents a significant leap forward in space assembly.
An assembler is essentially a group of “modular robots that work together and build things”.1 The use of modern control theory and machine learning allows the stacked platforms to be properly modular and reconfigurable while being capable of autonomous in-space assembly. This system can self-reconfigure, schedule tasks, and execute complex assembly operations with remarkable precision and minimal human interaction.
The machine learning component optimizes various assembly tasks and detects and addresses system faults. This technology promises high precision, fault tolerance, and modularity, making it ideal for future NASA missions.
Space Tech and AI
These NASA assemblers, could play a crucial role in upcoming space missions, showcasing NASA’s continued commitment to pushing the boundaries of space exploration. Aside from it applications for constructing structures in orbit or on the lunar surface, such as habitats, refueling stations, solar arrays, among others, this technology can also be used in advanced industrial manufacturing and assembly.
More space tech? Read more in our Space Technology Mini Patent Landscape Report
Tags: AI, artificial intelligence, machine learning, hexapod, in-space assembly, space technology, NASA patents