Artificial intelligence is transforming healthcare through groundbreaking technologies in diagnostics and patient care. Ellipsis Health’s speech-based AI system offers real-time mental health insights, while 4bases’ cfDNA biomarker detection enhances early identification of organ transplant rejection. These innovations exemplify the potential of AI to improve diagnostic accuracy and patient care across diverse medical fields.
CFDNA fragments as biomarkers after organ transplantation
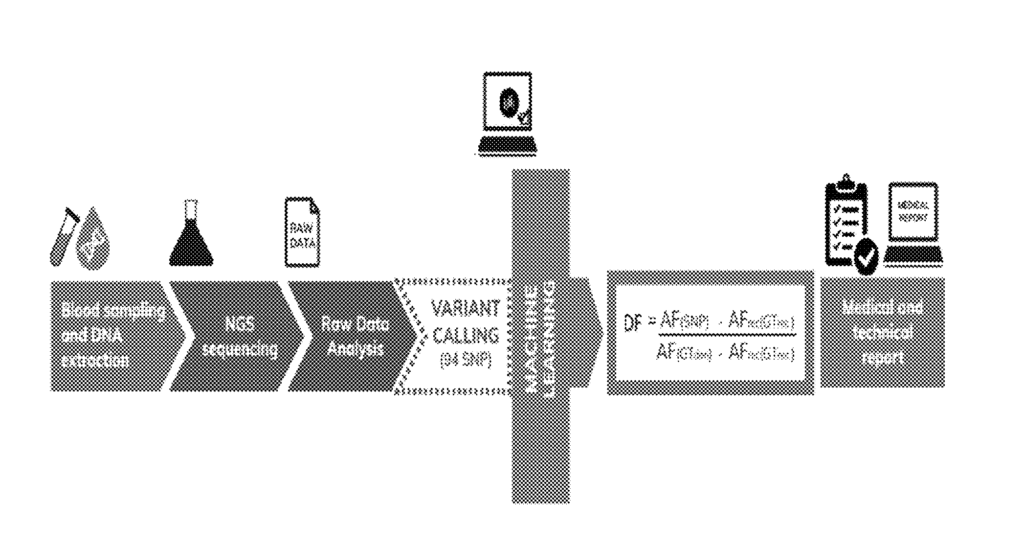
AI and advanced genomic technologies is revolutionizing the field of transplant medicine, offering new horizons for non-invasive diagnostics. 4bases primarily focuses on developing NGS-based diagnostic kits. Next-generation sequencing is a relatively new technology for “DNA or RNA sequencing and variant/mutation detection”.
The Swiss biotech has recently secured a patent for a novel method for detecting donor cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in the bloodstream of transplant recipients. The patented technology aims to improve the early identification of organ transplant rejection and to provide aid and guidance for post-transplant care. 4bases’ method offers a non-invasive alternative of using biomarkers to the traditional endomyocardial biopsy, the “gold standard” approach of doing invasive tissue biopsy procedures when it comes to monitoring organ rejection.
The patented method utilizes a panel of 94 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to differentiate between donor-derived and recipient-derived cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in a patient’s blood sample. During an immune response against a transplanted organ, the recipient’s body attacks the organ, causing the release of donor-derived cfDNA into the bloodstream. By sequencing these specific SNPs, the technology accurately quantifies the level of donor cfDNA, providing a direct measure of graft damage. Machine learning models, such as Naïve Bayes classifiers, are employed to analyze the sequencing data and identify unknown variables during the process. Based on their experiments, their method boasts a high sensitivity of over 98% and a low incidence of false negatives, making it a highly effective tool for monitoring transplant health.
With the ability to detect changes in the level of cfDNA over different time intervals, clinicians can promptly intervene and provide the appropriate care to organ transplant patients post-transplant. Immunosuppressive therapies may also be adjusted accounting for any rejection episodes, wherein an increase or a decrease in the level of cfDNA corresponds with a transplant rejection or a transplant tolerance, respectively. U.S. Patent No. 11,987,844 was filed on January 29, 2019 and was published on May 21, 2024.
Also read: Gene Therapy Patent Landscape Report
Speech-based AI system for real-time mental health insights
AI is also making significant strides in the realm of mental health, with more innovative applications emerging that enhance diagnostic accuracy and patient care. Ellipsis Health’s primary focus is on “vocal biomarker technology”. They have published various studies on AI-enabled, speech-based distress screening or depression detection and has several patents and patent applications on speech-based health assessment.
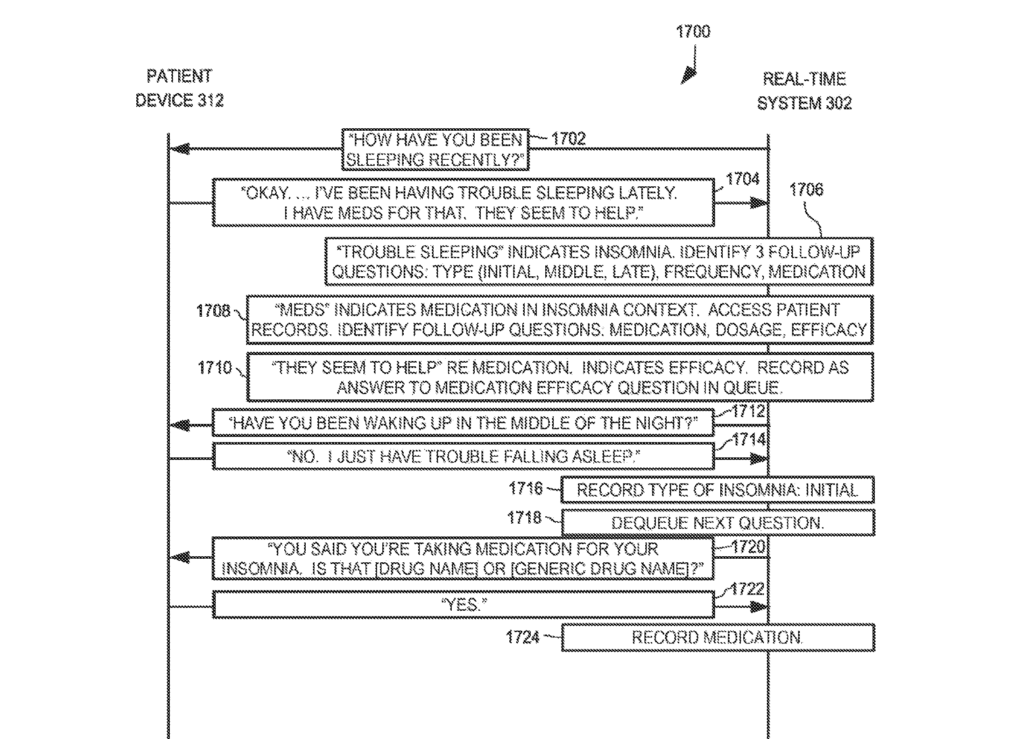
Their recent patent application describes a system and method for mental health assessment using speech data and machine learning models. The system fuses natural language processing (NLP) and acoustic outputs to generate a composite output, quantifying the risk of a condition with a confidence level.
The method involves presenting queries to subjects, updating scores based on responses, and assessing confidence levels. The system can be used to assess a patient’s mental state in real-time, providing an engaging and personalized approach compared to traditional screening tools like the PHQ-9, a common questionnaire used to detect or determine depression.